Cybersecurity Threats in Connected Medical Devices

Cybersecurity Threats in Connected Medical Devices
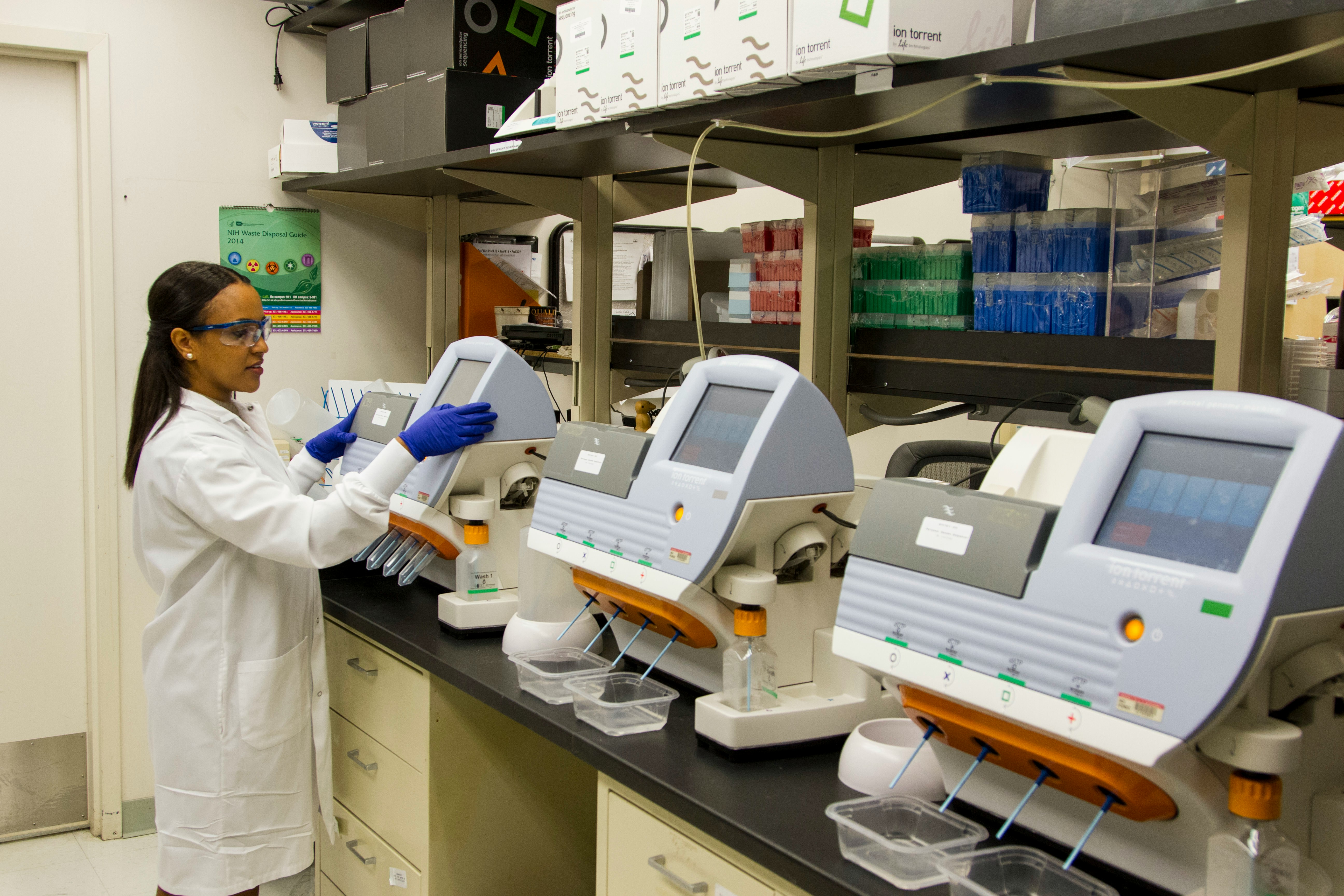
The integration of connected medical devices has revolutionized healthcare delivery, offering unprecedented levels of patient monitoring, diagnosis, and treatment. From wearable health monitors that track vital signs to complex diagnostic machines and therapeutic systems, these devices have become indispensable in modern healthcare. However, the interconnected nature of these devices also exposes them to cybersecurity threats, presenting risks to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of health information, as well as potential threats to patient safety. Cyberattacks on connected medical devices can lead to data breaches, unauthorized access to sensitive information, and even manipulation of device functionality, posing serious risks to patient care. To mitigate these risks, healthcare organizations must implement robust cybersecurity measures, including regular security assessments, encryption of data, and the use of secure authentication mechanisms. Additionally, the integration of best revenue cycle management software can help streamline billing processes, enhance revenue generation, and improve overall financial performance for healthcare organizations, ensuring that they can focus on delivering high-quality care while maintaining the integrity and security of their systems and data.
The Evolution of Connected Medical Devices
Connected medical devices are part of the broader Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), which encompasses a variety of devices such as insulin pumps, pacemakers, wearable fitness trackers, and remote patient monitoring systems. These devices collect, transmit, and receive health and medical information over a network, facilitating real-time data access for healthcare providers and patients. This evolution has enabled significant advancements in personalized medicine, early diagnosis, and the ability to monitor and manage chronic conditions outside of traditional healthcare settings.
Cybersecurity Threats to Connected Medical Devices
As the connectivity of medical devices expands, so too does the landscape of potential cybersecurity threats. These threats can be broadly categorized into unauthorized access, data breaches, and device tampering:
- Unauthorized Access: Connected medical devices can be vulnerable to unauthorized access, where attackers gain control over a device. This could lead to the unauthorized viewing or altering of sensitive health information, potentially resulting in privacy violations and identity theft.
- Data Breaches: Cyberattacks targeting the data transmitted or stored by these devices can lead to significant breaches of health information. Such breaches not only compromise patient confidentiality but also expose healthcare organizations to legal and financial repercussions.
- Device Tampering: Perhaps the most alarming threat is the potential for attackers to tamper with the functioning of a medical device. This can result in altered device settings or functions, potentially leading to incorrect diagnoses, inappropriate treatments, or direct harm to the patient.
Implications of Cybersecurity Threats
The implications of these cybersecurity threats are profound. Beyond the violation of privacy and the potential for financial loss, the most critical concern is patient safety. Cybersecurity incidents involving medical devices can directly impact the efficacy of treatments and even endanger lives. Moreover, such incidents can erode trust in healthcare providers and the technology they employ, potentially deterring patients from utilizing lifesaving medical devices or services.
Mitigating Cybersecurity Risks
Addressing the cybersecurity risks associated with connected medical devices requires a multi-faceted approach, involving stakeholders across the healthcare ecosystem:
- Manufacturers must prioritize security in the design and development of medical devices, incorporating robust encryption, authentication, and access control measures.
- Healthcare providers should implement strict policies and procedures for the use and management of these devices, including regular security assessments and updates.
- Regulatory bodies need to establish and enforce comprehensive cybersecurity standards for medical devices to ensure manufacturers and healthcare providers adhere to best practices.
- Patients must be educated about the potential risks and best practices for the use of connected health devices, including the importance of securing home networks and monitoring device activity.
Conclusion
The integration of connected medical devices into healthcare represents a significant advancement in medical technology, offering unprecedented opportunities for enhancing patient care. However, the accompanying cybersecurity threats cannot be overlooked. By understanding these threats and implementing robust security measures, the healthcare industry can safeguard against cyber risks, ensuring the reliability and safety of these essential technologies. The collaborative effort of manufacturers, healthcare providers, regulatory bodies, and patients is crucial in creating a secure and trustworthy environment for the use of connected medical devices.



 WhatsApp Spy
WhatsApp Spy Facebook & Messenger Spy
Facebook & Messenger Spy Viber Spy
Viber Spy Instagram Spy
Instagram Spy Skype Spy
Skype Spy TikTok Spy
TikTok Spy Telegram Spy
Telegram Spy LinkedIn Spy
LinkedIn Spy Twitter Spy
Twitter Spy Youtube Spy
Youtube Spy Photo Spy
Photo Spy Video Spy
Video Spy Calls and Contacts Tracking
Calls and Contacts Tracking SMS & IM Chats
SMS & IM Chats Voice Capture
Voice Capture Image Capture
Image Capture Video Record
Video Record